We use electricity daily, but understanding how much it costs can be confusing. When we get our electricity bill, it often has different types of charges, rates, and numbers that can be hard to understand. Knowing how these things work can help you save money and make good choices about using electricity. This guide will explain how to figure out the electric bill, how to calculate your electricity cost and provide some simple tips to help you reduce your energy bills.

Components Of An Electricity Bill
How to figure out the electric bill cost? Understanding your electricity bill involves knowing its different parts and how they affect the total amount you owe.
Meter Reading
The meter reading indicates the total electricity consumed over the billing period. Electricity usage is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Your meter reading is essential for determining how much energy you've used.
Cost per kilowatt-hour (kWh)
This is the price you pay for each unit of electricity. It is often listed on your bill and can vary depending on your tariff plan and energy supplier. For example, if the cost is 30 pence per kWh, that's the amount you pay for each kilowatt-hour of electricity you use.
Tariffs and Charges
Your electricity bill may include various tariffs and additional charges. Tariffs can be fixed (where you pay a constant rate) or variable (where the rate changes). Additional charges may include delivery fees, environmental surcharges, or taxes. These can significantly impact the total amount of your bill.
Total Amount Due
This is the final sum you owe for the billing period. It includes the cost of the electricity used, any extra charges, and applicable taxes. This amount is usually the most straightforward number on your bill, but understanding how it was calculated can help you manage your energy use better.
Calculating Your Electricity Bill
How to calculate the electric bill? Calculating your electricity bill involves a few straightforward steps that help you understand how much you pay and why. First, you need to find your meter readings. Check the readings on your electricity meter at the start and end of your billing period. Subtract the starting reading from the ending reading to determine the total electricity you've used during the period. This usage is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), the standard unit for electricity consumption.

Next, multiply your total kWh by the cost per kilowatt-hour, which is listed on your bill. For example, if your meter shows you've used 400 kWh and the rate is 30 pence per kWh, the calculation would be:
400 kWh×0.30 GBP/kWh=120 GBP
This amount reflects the base cost of the electricity you consume.
After determining the base cost, you need to add any additional charges or fees that may be listed on your bill. These could include delivery charges, regulatory fees, or other service costs. Add these extra charges to your base cost for a more accurate total.
Finally, combine the base cost and additional charges to determine the due amount. This final figure is the amount you must pay for your electricity usage during the billing period. Understanding these calculations can help you keep track of your electricity expenses and make informed decisions about your energy use.
Estimating The Cost Of Electrical Appliances
Estimating the cost of running electrical appliances involves a few simple calculations. Start by checking the appliance's power rating, typically listed in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW) on the appliance's label or user manual. For instance, a washing machine might have a power rating of 1,000 watts or 1 kilowatt. Next, determine how long you use the appliance. If you use the washing machine for 1 hour daily, you must calculate the total energy consumption.
How to figure out the electric bill? Multiply the appliance's power rating by the hours it operates each day. For a washing machine with a 1 kW rating running for 1 hour daily, the daily energy consumption is:
1 KW × 1 hour = 1 KWh
To find out how much this costs, multiply the daily energy consumption by the cost per kilowatt-hour (kWh) listed on your electricity bill. If your rate is 30 pence per kWh, the daily cost would be:
1 KWh × 0.30 GBP/kWh = 0.30 GBP/day
To get a monthly cost estimate, multiply the daily cost by the number of days in a month. For a 30-day month, the calculation is:
0.30 GBP/day × 30 days = 9.00 GBP/month
This method can be applied to any appliance. It helps you understand which devices are more expensive and allows you to manage your energy use more effectively.
Factors Affecting Electricity Costs
Several factors can influence how much you pay for electricity:
Type Of Tariff
As mentioned earlier, the type of tariff you are on can affect your electricity costs. Fixed-rate tariffs offer stability but might not be the cheapest option if prices drop. Depending on market conditions, variable-rate tariffs can fluctuate, saving money or costing more.
Time Of Use
If you are on a time-of-use tariff, the time of day you use electricity can impact your costs. Using more electricity during peak times can result in higher bills while shifting your usage to off-peak times can save money.
Location
Where you live can affect your electricity costs due to differences in regional distribution charges and taxes. Rural areas or places with older infrastructure might have higher delivery costs.
Energy Efficiency Of Your Home
Well-insulated homes that use energy-efficient appliances tend to have lower electricity costs. Poor insulation, inefficient appliances, and leaving lights or devices on can increase usage and bills.
Weather
Cold weather can increase electricity use if you rely on electric heating. Similarly, hot weather can lead to higher electricity bills due to increased use of air conditioning or fans.
Energy Supplier
Different suppliers offer different rates and tariffs. Switching to a supplier with a lower rate or a better-suited tariff can significantly reduce your electricity costs.
Government Policies And Taxes
Changes in government policies, regulations, and taxes can also affect the cost of electricity. For example, levies for renewable energy or carbon taxes can be added to your bill.
Tips For Saving Money On Your Electricity Bill
Saving money on your electricity bill can be more straightforward than you think. Here are some simple tips that can help you cut costs:
Turn Off Lights And Appliances When Not In Use
One of the simplest ways to save electricity is to turn off lights and appliances when you're not using them. It can include everything from lights in unoccupied rooms to TVs, computers, and kitchen appliances.
Use Energy-Efficient Appliances
Look for appliances with an energy-efficient rating. These appliances use less electricity to perform the same tasks as their less efficient counterparts, and the savings can be significant over time.
Install A Smart Thermostat
A smart thermostat can automatically adjust your home's temperature according to your schedule. It ensures that you're not heating or cooling your home when it's not needed, which can save a lot of electricity.
Take Advantage Of Off-Peak Rates
If your electricity plan offers cheaper rates during off-peak hours, try to run energy-intensive appliances like washing machines, dryers, and dishwashers during those times.
Use LED Bulbs
LED bulbs use up to 90% less electricity than traditional incandescent bulbs and last much longer. Replacing your home's lighting with LEDs can result in noticeable savings on your electricity bill.
Improve Home Insulation
Sound insulation in walls, roofs, and floors can reduce the heating and cooling needed to keep your home comfortable. It can also lower electricity usage and costs, especially during extreme weather conditions.
Unplug Devices
How to work out utility bills? Devices and chargers plugged in but not in use can still draw small amounts of power, often called "phantom" or "standby" power. Unplugging devices when they're not needed can help reduce this unnecessary usage.
Consider Renewable Energy Options
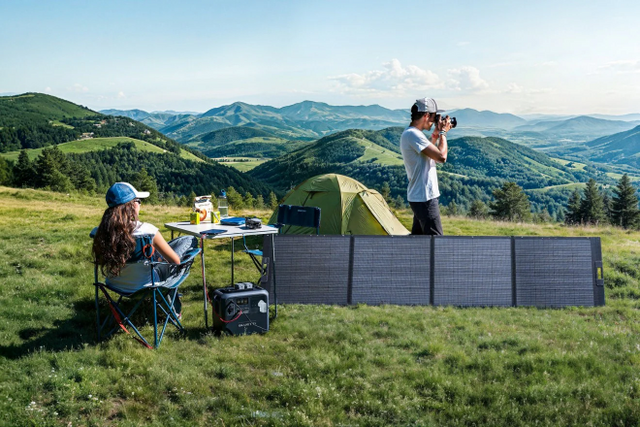
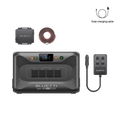
The BLUETTI AC200L + PV200 is a great option for daily use and emergencies. This portable power station has a large battery capacity, multiple ways to charge, and smart features, making it a reliable and eco-friendly choice to keep your devices charged and ready.

With a 2,048-watt-hour (Wh) battery and a 2,400-watt continuous output, it is designed to handle various power needs, from daily use to emergency backup. The BLUTTTI AC200L + PV200 can be expanded with additional batteries, increasing its capacity to 8,192 Wh, making it suitable for short-term and extended power requirements.
This model supports charging methods, including AC, solar, and car inputs. Its ability to harness solar energy is particularly noteworthy, with a 1,200-watt solar input capacity allowing efficient recharging from sunlight. The BLUETTI AC200L + PV200 also features intelligent control through the BLUETTI app, enabling users to monitor and manage their power usage from a distance.

The AC200L + PV200, BLUETTI provides high-efficiency solar panels to complement their power stations. These panels effectively convert sunlight into electricity, providing a renewable and sustainable energy source. BLUETTI's battery backup systems, using durable lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO₄) batteries, offer long-lasting performance and can be scaled up with additional units to meet more significant energy needs.
Conclusion
How to work out your electricity bill? Learn about the different parts of the bill, how to calculate costs, and the factors that affect electricity prices to make smarter choices and save money. Simple changes, like using energy-efficient appliances and taking advantage of off-peak rates, can also help lower your bill. Consider the BLUETTI AC200L + PV200 solar generator for a more effective solution. It can help you generate power and reduce electricity costs, contributing to a more sustainable future.
Shop products from this article
You May Also Like

Sodium-Ion vs Lithium-Ion Battery: The Real Science behind Cold Weather Battery Drain
Why is sodium-ion battery often considered more reliable in winter? Do you know the real science behind it? In this guide, you will explore the comparison between lithium-ion and sodium-ion...

Oven Power Consumption Explained: How Much Electricity Does Your Oven Use?
Have you ever thought about how much electricity your oven uses? What's the power rating in UK homes, or the associated cost with it? Discover some tips to reduce your...

Is the UK's Power Grid at Risk of Blackout?
Learning from Iberia's 14-hour blackout. With 40% renewable energy, Britain faces similar grid stability challenges. Discover how home energy storage solutions like BLUETTI provide critical backup power and enhance grid...