In our world today, where we rely on batteries for so many things, understanding how they work is important. One key thing to know about batteries is their voltage, battery voltage is like the fuel gauge in a car. It tells us how much energy is stored in the battery and how strong the electrical push that it can give to power devices. In this guide, we're going to learn all about battery voltage charts and why it's so important.
What is Battery Voltage?
Battery voltage refers to the measure of electrical potential difference between the positive and negative terminals of a battery. It indicates the amount of electrical energy stored within the battery and determines the force with which electrons flow through an electrical circuit when the battery is connected to a load. In simpler terms, battery voltage represents the "push" or pressure that drives the flow of electricity from the battery to power devices or systems.
Voltage is typically measured in volts (V), and it plays a critical role in determining the performance characteristics of a battery. Different types of batteries have varying voltage levels, which are determined by their chemical composition and design. For instance, common household batteries like AA or AAA batteries typically have a voltage of 1.5 volts each. The larger batteries used in electric vehicles or renewable energy storage systems can have much higher voltages, often in the hundreds of volts.
State of Charge and Discharge (SOC & SOD)
State of Charge (SOC) and State of Discharge (SOD) are essential parameters used to describe the energy level of a battery relative to its maximum capacity. Understanding SOC and SOD is crucial for effectively managing battery usage, optimising performance, and prolonging battery life.
State of Charge (SOC):
State of Charge (SOC) refers to the percentage of a battery's maximum capacity that is currently available for use. It represents the amount of energy stored in the battery relative to its full charge capacity. SOC is typically expressed as a percentage, with 100% indicating a fully charged battery and 0% indicating a fully discharged battery.
Monitoring SOC is Essential for Several Reasons:
Knowing the SOC helps users determine when to recharge the battery to ensure the uninterrupted operation of devices or systems. Allowing a battery to discharge below a certain SOC threshold can cause irreversible damage, reducing battery lifespan. Monitoring SOC helps prevent over-discharge and prolong battery life. SOC data can be used to predict the remaining runtime of a battery-powered device or system, allowing users to plan accordingly.
State of Discharge (SOD):
State of Discharge (SOD) complements SOC by indicating the percentage of a battery's energy that has been consumed relative to its maximum capacity. Like SOC, SOD is also expressed as a percentage, with 100% indicating complete discharge and 0% indicating a fully charged battery.
Why it’s important to understand SOD:
Monitoring SOD helps users avoid draining the battery beyond safe limits, which can lead to performance degradation or damage. Limiting the depth of discharge (DoD) – the percentage of a battery's capacity that is discharged during each use cycle – can extend the overall lifespan of the battery. Monitoring SOD allows users to manage DoD effectively.
Keeping SOD within safe limits ensures that the battery maintains optimal performance and reliability over time.
Importance of SOC and SOD:
SOC and SOD are critical for effective battery management, allowing users to maximise performance, efficiency, and lifespan. Monitoring SOC and SOD helps prevent overcharging, over-discharging, and other conditions that can compromise battery safety. By understanding SOC and SOD, you can optimise battery usage to meet specific requirements, whether for portable electronics, electric vehicles, or renewable energy systems.
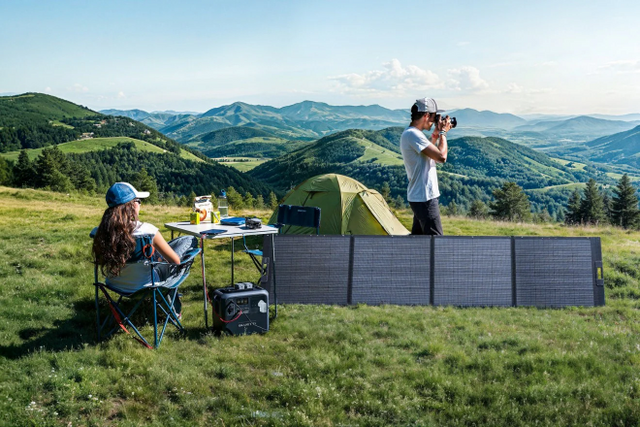
BLUETTI AC200L: Efficient Output, Unparalleled Convenience
The BLUETTI AC200L battery is renowned for its exceptional Depth of Discharge (DoD) capabilities, making it a standout choice for various portable power applications. DoD refers to the percentage of a battery's total capacity that can be safely discharged during each use cycle without causing damage or significantly reducing lifespan. The higher the DoD, the more energy users can extract from the battery before recharging it.

BLUETTI AC200L boasts an impressive 95% DoD, setting it apart from many other battery systems on the market. This means that users can utilise up to 95% of the battery's total capacity before needing to recharge, providing extended runtime and greater flexibility in powering various devices and appliances.
Key Features of BLUETTI AC200L:
High Capacity: The BLUETTI AC200L offers a substantial energy storage capacity of 2,048 watt-hours (Wh), ensuring ample power for prolonged usage.
Expandable: For users with higher energy requirements, the BLUETTI AC200L is expandable, allowing for additional battery modules to be connected. With the addition of extra modules, the total capacity can be increased to 4,096Wh with 1×B230, 8,192Wh with 2×B300, or 6,348Wh with 2×B210.
Fast Recharging: The BLUETTI AC200L supports rapid recharging, with the ability to replenish from 0% to 80% capacity in just 45 minutes using a 2,400W AC input. This feature ensures minimal downtime between uses, enhancing overall convenience and productivity.
Versatile Charging Options: With multiple charging methods available, including AC, solar, car, generator, lead battery, and a combination of AC and solar, the BLUETTI AC200L offers versatility and adaptability for various charging scenarios.
Smart Control and Monitoring: Users can conveniently control and monitor the BLUETTI AC200L via the BLUETTI app, accessible through Bluetooth and Wi-Fi connectivity. This feature provides real-time data on battery status, power consumption, and charging progress, allowing for efficient management and optimization of power usage.
Quiet Operation and UPS Functionality: The BLUETTI AC200L operates quietly, ensuring minimal disturbance in indoor environments. Additionally, it features a 20ms uninterruptible power supply (UPS) function, providing seamless power backup during outages or fluctuations in the grid supply.
High Efficiency: With its advanced design and technology, the BLUETTI AC200L delivers high efficiency in energy conversion and utilisation, maximising overall performance and minimising energy wastage.
Battery Voltage Charts
Car battery voltage charts provide valuable information about the voltage levels of different types of batteries at various states of charge (SOC). These charts are essential for understanding the voltage characteristics of batteries and help monitor, manage, and optimise battery usage. Here are battery voltage car charts for several common types of batteries:
Lead Acid Battery Voltage Chart
Lead-acid batteries are the earliest type of rechargeable battery chemistry and have been the standard for consumer applications for decades.
Lead-acid batteries, which are commonly used in petrol and diesel cars, provide the enormous bursts of energy required to start engines. While cheaper, they have a lower energy density and a shorter lifespan than modern technologies, necessitating constant maintenance to assure longevity.
|
Capacity |
6V Sealed Lead Acid Battery |
6V Flooded Lead Acid Battery |
|
100% |
6.44V |
6.32V |
|
90% |
6.39V |
6.26V |
|
80% |
6.33V |
6.20V |
|
70% |
6.26V |
6.15V |
|
60% |
6.20V |
6.09V |
|
50% |
6.11V |
6.03V |
|
40% |
6.05V |
5.98V |
|
30% |
5.98V |
5.94V |
|
20% |
5.90V |
5.88V |
|
10% |
5.85V |
5.82V |
|
0% |
5.81V |
5.79V |
Lithium-ion Battery Voltage Chart
Lithium-ion batteries are common in current gadgets due to their high energy density and lightweight design. They are widely used in portable electronics and electric vehicles, providing longer lifespans and superior performance to standard batteries.
Lithium-ion batteries are the favoured choice for many applications due to their efficiency and quick charging capabilities. Lithium-ion battery voltage chart:
|
Capacity (%) |
1 Cell |
12 Volt |
24 Volt |
48 Volt |
|
100 |
3.40 |
13.6 |
27.2 |
54.4 |
|
90 |
3.35 |
13.4 |
26.8 |
53.6 |
|
80 |
3.32 |
13.3 |
26.6 |
53.1 |
|
70 |
3.30 |
13.2 |
26.4 |
52.8 |
|
60 |
3.27 |
13.1 |
26.1 |
52.3 |
|
50 |
3.26 |
13.0 |
26.0 |
52.2 |
|
40 |
3.25 |
13.0 |
26.0 |
52.0 |
|
30 |
3.22 |
12.9 |
25.8 |
52.5 |
|
20 |
3.20 |
12.8 |
25.6 |
51.2 |
|
10 |
3.00 |
12.0 |
24.0 |
48.0 |
|
0 |
2.50 |
10.0 |
20.0 |
40.0 |
LiFePO4 Battery Voltage Chart
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4/LFP) batteries have higher safety ratings, faster recharge times, and a longer lifespan than regular lithium-ion batteries.
LFP batteries, with their extraordinarily long cycle life, great depth of discharge, and wide operating temperature range, are quickly becoming the preferred chemistry in EVs and home backup battery systems.
LiFePO4 batteries are more environmentally friendly and ethically sourced than ordinary Li-ion batteries. LFP does not require nickel or cobalt, which are mined in the Democratic Republic of the Congo under harsh working conditions.
|
Capacity |
12V |
24V |
48V |
|
100% (charging) |
14.6V |
29.2V |
58.4V |
|
100% (resting) |
13.6V |
27.2V |
54.4V |
|
99% |
13.4V |
26.8V |
53.6V |
|
90% |
13.3V |
26.6V |
53.2V |
|
70% |
13.2V |
26.4V |
52.8V |
|
40% |
13.1V |
26.2V |
52.4V |
|
30% |
13.0V |
26.0V |
52.0V |
|
20% |
12.9V |
25.8V |
51.6V |
|
17% |
12.8V |
25.6V |
51.2V |
|
14% |
12.5V |
25.0V |
50.0V |
|
9% |
12.0V |
24.0V |
48.0V |
|
0% |
10.0V |
20.0V |
40.0V |
Deep Cycle Battery Voltage Chart
Deep cycle batteries are intended to supply consistent power over long periods. They outperform standard lead-acid batteries in applications needing consistent energy output, such as renewable energy systems or recreational vehicles.
Compared to typical flooded lead acid (FLA) batteries, modern valve-regulated lead-acid (VRLA) deep cycle battery technologies such as AGM and Gel have a deeper discharge. They often last longer and require less maintenance than FLA batteries.
|
Capacity |
12V |
24V |
48V |
|
100% (charging) |
13.00V |
26.00V |
52.00V |
|
99% |
12.80V |
25.75V |
51.45V |
|
90% |
12.75V |
25.55V |
51.10V |
|
80% |
12.50V |
25.00V |
50.00V |
|
70% |
12.30V |
24.60V |
49.20V |
|
60% |
12.15V |
24.30V |
48.60V |
|
50% |
12.05V |
24.10V |
48.20V |
|
40% |
11.95V |
23.90V |
47.80V |
|
30% |
11.81V |
23.62V |
47.24V |
|
20% |
11.66V |
23.32V |
46.64V |
|
10% |
11.51V |
23.02V |
46.04V |
|
0% |
10.50V |
21.00V |
42.00V |
AGM Battery Voltage Chart
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4/LFP) batteries have higher safety ratings, faster recharge times, and a longer lifespan than regular lithium-ion batteries. LFP batteries, with their extraordinarily long cycle life, great depth of discharge, and wide operating temperature range, are quickly becoming the preferred chemistry in EVs and home backup battery systems.
LiFePO4 batteries are more environmentally friendly and ethically sourced than ordinary Li-ion batteries. AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) batteries, a type of lead-acid battery, are renowned for their efficiency and longevity. They require little maintenance and may withstand higher temperatures than conventional lead-acid batteries. AGM batteries are widely employed in backup power systems and off-grid applications due to their consistent performance and long service life. Here is the AGM battery voltage chart:
|
Capacity |
12V |
24V |
48V |
|
100% (charging) |
13.0V |
26.00V |
52.00V |
|
100% (resting) |
12.85V |
25.85V |
51.70V |
|
99% |
12.80V |
25.75V |
51.45V |
|
90% |
12.75V |
25.55V |
51.10V |
|
80% |
12.50V |
25.00V |
50.00V |
|
70% |
12.30V |
24.60V |
49.20V |
|
60% |
12.15V |
24.30V |
48.60V |
|
50% |
12.05V |
24.10V |
48.20V |
|
40% |
11.95V |
23.90V |
47.80V |
|
30% |
11.81V |
23.62V |
47.24V |
|
20% |
11.66V |
23.32V |
46.64V |
|
10% |
11.51V |
23.02V |
46.04V |
|
0% |
10.50V |
21.00V |
42.00V |
People Also Ask about Battery Voltage
What voltage is considered a bad battery?
A battery with a significantly lower voltage than its rated voltage or one that cannot maintain a 12V battery voltage chart under load is typically considered bad.
At what voltage is a 12V battery dead?
A 12V battery is considered dead when its voltage drops below 10.5 volts under load.
What is the voltage of a 12V battery when fully charged?
A fully charged 12V battery typically has a voltage between 12.6 to 12.8 volts.
What voltage is a 12V battery at 50%?
A 12V battery at a 50% state of charge typically has a voltage of around 12.2 volts.
Conclusion
Battery voltage is a fundamental aspect of battery technology that significantly impacts performance, safety, and usability. Understanding concepts such as the State of Charge and Discharge, as well as the voltage characteristics of different battery types, is essential for maximising efficiency, prolonging battery life, and ensuring safe operation.
Whether for consumer electronics, automotive applications, or renewable energy systems, knowledge of battery voltage is indispensable in our increasingly electrified world. Due to its amazing DoD abilities and many other advantages for portable power stations, the BLUETTI AC200L battery is the best option.
Shop products from this article
You May Also Like

Fridge Temperature Guide: What Temperature Should a Fridge Be?
Temperature management is crucial for the performance of the fridge. Find out at what temperature the fridge should be, the ideal range between 1-5°C, customised tips for winter, and the...

Winter Fuel Payment: Eligibility, Payment Dates, and Winter Energy Tips
Winter Fuel Payments are the best source for pension-age households to manage rapidly increasing winter energy costs. Explore more on the eligibility, payment dates, allowance amounts, and practical winter energy...

Sodium-Ion vs Lithium-Ion Battery: The Real Science behind Cold Weather Battery Drain
Why is sodium-ion battery often considered more reliable in winter? Do you know the real science behind it? In this guide, you will explore the comparison between lithium-ion and sodium-ion...