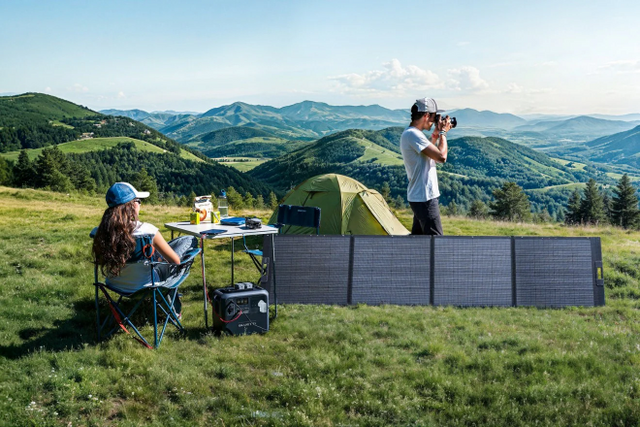
Lithium-ion batteries have become an integral part of our daily lives, powering everything from smartphones and laptops to power tools and electric vehicles. While these batteries offer incredible energy density and efficiency, improper storage can pose significant risks. Understanding the nuances of storing lithium battery storage is crucial for both safety and optimal performance. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of lithium-ion battery storage, addressing key questions, rules, and recommendations to ensure safe and effective handling.
The Importance of Knowing How to Store Lithium Batteries
How to store lithium batteries? Storing lithium batteries is paramount due to their widespread use and the potential risks associated with improper storage. As essential components in devices ranging from smartphones to electric vehicles, lithium-ion batteries have become indispensable in our daily lives.
However, their chemical composition and energy density make them susceptible to safety hazards if mishandled or stored incorrectly. Understanding the nuances of lithium-ion battery storage regulations in the UK is not just a matter of convenience; it is a fundamental aspect of responsible technology use and a crucial step in ensuring the safety of individuals and the longevity of these power sources.
As the demand for lithium-ion batteries continues to rise, so does the need for proper disposal and recycling. Safe storage practices can mitigate the risk of battery malfunctions, leaks, or fires, reducing the likelihood of environmental contamination. Moreover, by extending the lifespan of lithium batteries through appropriate storage, we contribute to a more sustainable approach to energy consumption, minimizing the need for frequent replacements and reducing electronic waste.

In a broader context, the knowledge of lithium-ion battery storage is essential for industries and businesses that rely on these batteries to power critical operations. From emergency backup systems to renewable energy storage, the correct storage of lithium batteries ensures the reliability of these systems when they are most needed. The economic impact of downtime or failures due to improperly stored batteries can be substantial, making it imperative for businesses to invest in proper storage infrastructure and educate their personnel on best practices. In essence, the importance of knowing how to store lithium batteries transcends individual users, encompassing environmental, societal, and economic considerations.
Storing Lithium Battery: Charge or Discharge?
Batteries used to need to be charged before being placed in long-term storage because they were all susceptible to high levels of self-discharge, which might cause irreparable damage like significant capacity loss or even render the battery unusable.
Why Charging Your Lithium-Ion Battery Before Storing It Is Not a Good Idea?
Lithium-ion batteries are now the industry standard in battery technology, and their self-discharge is essentially nonexistent. Lithium-ion batteries are typically constructed with discrete inbuilt fuses that can automatically transition a heavily depleted battery to a rest state, protecting cells from over-discharge and eliminating the need for a complete charge before storage.
Lithium-ion batteries have a longer lifespan if they are stored partially charged. However, it's important to keep in mind that cells will not survive well if the battery is fully charged or stored at a very low level of charge. To minimize aging and self-discharge, we advise storing a lithium-ion battery with two lit LEDs, indicating a charge of 40–60%.
The Self-Discharge Rate of Outdated Battery Technology is Considerable
Due to their high rates of self-discharge, older battery types used in automobiles, such as lead or nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries, are more likely to overcharge after extended periods of inactivity. When the battery's charge level drops below the cut-off voltage, this is what happens. When this occurs, there is no longer any source of energy, and the battery may not charge. Because of this, battery care guidelines recommend monitoring the remaining charge frequently and fully charging before any extended periods of storage.
Modern Lithium-Ion Battery Technology Guards Against Excessive Discharge
Modern lithium-ion battery batteries are made of lithium-ion cells and have incredibly low rates of self-discharge—just 1% to 3% per year when they are stored. Furthermore, every battery comes with an advanced BMS Battery Management System. It avoids over-discharge by monitoring the voltage in each integrated cell within a battery. Should the voltage in the lithium-ion battery cells drop too low, the battery will immediately transition to a rest state, stopping the discharge process.
BLUETTI battery is made of lithium-ion cells with low self-discharge and BMS. Moreover, it is equipped with high-end technology, which makes it be stored in your house safely.

Rules to Store and Protect Lithium Battery
Ensuring the safe storage of lithium-ion batteries involves adhering to specific rules and guidelines. Implementing these rules mitigates potential risks and fosters an environment conducive to maintaining battery health.
Before storing your cordless power tool:
- Take out the battery.
- Verify the battery's charge level and that both of its LEDs are lighted.
- If necessary, clean the batteries of dirt and grime with a moist cloth.
- Keep the batteries somewhere dry and out of the sun—in a closed box, for instance.
- Temperature requirements: dry basements, garages, or well-insulated sheds are good places to store batteries since they keep them at a temperature between -10°C and 50°C.
- Make sure your lithium-ion batteries are kept out of children's reach by keeping them in a secure location.
- Keep the battery and charger apart and in a temperature range of 5 to 40 degrees Celsius.
People Also Ask about Lithium Battery Storage
Is it Safe to Store Lithium Batteries in the House?
Storing lithium batteries in the House is generally safe when proper precautions are taken. Additionally, considering advanced power storage solutions like the BLUETTI EP500Pro can enhance safety measures. The BLUETTI EP500Pro is equipped with advanced battery management systems, ensuring secure and efficient storage of power for various applications.
The main characteristic of LiFePO4 batteries is their strong safety profile, which is the product of their extremely stable chemistry—a quality that lead-acid and most other battery types lack. When the conventional NCA/NCM battery deflagrates and catches fire in the experimental conditions (high temperature and acupuncture), the lithium iron phosphate battery in identical conditions merely generates a small amount of smoke and doesn't produce any visible flame.

LiFePO₄ batteries are capable of 100% depth of discharge (DOD) in addition to 3,000–5,000 cycles or more. Why is that relevant? It implies that, in contrast to other batteries, LiFePO₄ eliminates the risk of overcharging your battery. As a result, you can use it for extended periods. Lead acid batteries, on the other hand, only have a 300–400 cycle life. The mid-to-high-end power station of BLUETTI uses premium lithium iron phosphate batteries, which have a 3,500 charge-discharge cycle.
Is it Best to Keep Lithium Batteries Fully Charged?
The ideal state for long-term storage of lithium batteries is around 40-60% charge. Fully charging lithium batteries before storage may be recommended for certain technologies that incorporate protection against over-discharge. However, keeping them at a moderate charge level minimizes stress on the battery and promotes longevity.
How Long Can Lithium-Ion Batteries Be Stored?
The shelf life of lithium-ion batteries varies based on factors such as temperature, charge level, and overall battery health. When stored in optimal conditions—cool, dry, and at a moderate charge level—lithium-ion batteries can retain a significant portion of their capacity even after several years. Regularly checking and maintaining the batteries, as outlined in the rules above, contributes to prolonged storage life.
Conclusion
Proper storage of lithium-ion batteries is essential for safety, performance, and longevity. Whether it's deciding whether to charge or discharge before storage, following specific rules for storage, or addressing common questions about storing lithium-ion batteries, informed decisions can lead to a more secure and efficient use of these powerful energy sources.
By understanding the nuances of lithium-ion battery storage and adhering to manufacturer guidelines, users can ensure that these batteries continue to power our devices, tools, and vehicles reliably and safely. As technology advances, incorporating innovative solutions like the BLUETTI EP500Pro can further enhance the safety and convenience of storing lithium-ion batteries in various settings. Ultimately, responsible and informed practices in lithium battery storage contribute to a more sustainable and efficient use of this transformative energy technology.
Shop products from this article
You May Also Like

Fridge Temperature Guide: What Temperature Should a Fridge Be?
Temperature management is crucial for the performance of the fridge. Find out at what temperature the fridge should be, the ideal range between 1-5°C, customised tips for winter, and the...

Winter Fuel Payment: Eligibility, Payment Dates, and Winter Energy Tips
Winter Fuel Payments are the best source for pension-age households to manage rapidly increasing winter energy costs. Explore more on the eligibility, payment dates, allowance amounts, and practical winter energy...

Sodium-Ion vs Lithium-Ion Battery: The Real Science behind Cold Weather Battery Drain
Why is sodium-ion battery often considered more reliable in winter? Do you know the real science behind it? In this guide, you will explore the comparison between lithium-ion and sodium-ion...