Your house's average electricity usage can depend on different factors, from location to size, or to the ways you use your appliances. However, there are certain ways to lower the cost of your electricity usage, and if you keep reading you will understand how to do so.
How Many kWh Does the Typical UK Home Use Each Day?
On average, a UK home has 2 to 3 occupants and according to Ofgem, it uses on average 8 kWh of electric power daily. This means that yearly one home spends 2,900 kWh, which is 242 kWh monthly. But this is just an estimate and can differ from home to home.
Although this is the statistic for the average electricity usage, this doesn’t mean that there is a number you should keep in mind without further analysis of your own home. You can anticipate more significant bills if you have devices that use quite a lot of electricity or just a large number of these devices. The temperature and length of time that you have your heating on also plays a bigger role than ever in the electricity usage of your home.
How Much Do Average UK Appliances Cost?
According to OVO energy, some UK appliances have surprisingly high costs that you might not be aware of. Make sure to turn off everything you don’t use in order to save on these costs.
Light
You will already be saving money each year if you have upgraded the lighting in your home to LED. LED lighting consumes 9kWh per year at a cost of £2.52 based on a daily usage average of two hours. However, halogen light bulbs use an average of 31kWh each year, which costs £8.68, so you might want to switch if you still use them.
It should come as no surprise that LED light bulbs save money because they are more effective with where the energy produced is directed. Halogen light bulbs spend the majority of their energy on heat, but LEDs do not become hot and use the majority of their energy on light—they also last longer!
TV
According to estimates, a 32" LED TV uses 50kWh annually when used for four hours per day. However, an LCD flat screen costs £55.72 each year and consumes 199kWh. Again, current new LED technology and enhanced efficiency ratings are to blame for the sharp increase. If you are investing, switch to LED TVs to save money each year or give yourself a few more hours to watch TV.

Fridge and Freezer
One of the appliances in your home that is always turned on is the refrigerator/freezer. The most expensive appliances to operate are combo fridge-freezers; a typical combi uses 427kWh per year and costs £119.56 to run.
But if you have a combination refrigerator and freezer with an A+ energy rating, it will probably require about 200kWh per year, which costs £56. When purchasing an appliance, it's crucial to consider its energy rating because doing so can help you save money in the long run.
Cooker
Type, energy rating, and usage all affect how much energy a cook uses. The average annual cost of 317kWh used by electric stoves is £88.76.
Washing Machine
The high electricity consumption of washing machines is not surprising. Your machine might be using 166kWh per year, which would cost you £46.48, based on the average number of cycles per home which is 270 per year. Depending on the spin cycle, temperature, size of the load, and efficiency rating, each cycle can vary between 0.3kWh and 1kWh.
Tumble Dryer
With an average of 150 cycles per year, a tumble dryer in your home may be using 394kWh annually, which would cost you £110.32. The price can change based on how frequently you use it, the type of dryer you use, the amount of the load, the setting, and the appliance's energy efficiency rating.
What Factors Into My Electricity Costs?
Every electricity bill is different and depends on a number of factors. Here are some of the main reasons why your invoice looks the way it does:
Location
According to Ofgem, electricity bills are dependent on your location in the UK, because some postcodes are a lot more expensive than others. Not only are there different energy providers you can choose from, but the same provider may charge different rates depending on the city you live in.
Home Size
Bigger homes have more lights and appliances. They’re also usually homes to larger families. All of this can affect your electricity bill, so think of downsizing if your bill is too high.
How Many People Are Living in the House
When there are more people in the house there is more cooking, washing, and hot water used, so all of these factors can greatly affect your electricity bills.
When Was the House Built
Better insulation, more effective electricity usage and even solar panels are often features of newer construction. If your house is older you may want to consider how renovation could help to lower your energy bills.
How to Know if You Are a High-Energy User?
Because the home size and the number of occupants are the usual causes that can determine high energy use, it can be difficult to track your specific energy use. Even the lifestyle can be a cause of large energy use, including remote work where individuals use a lot more energy because they spend more time at home.
A one to two-bedroom apartment with just one or two other people can use as little as 1,900 kWh monthly on average. If your home has four rooms and four to five residents you can use up to 4,600 kWh monthly, or even more if you are spending a lot of time at home, cooking at home, and have kids that spend a lot of time on TV and computers.
Most energy suppliers in the UK provide smart meters to customers free of charge. Get in touch with your energy company to ask about smart meter installation so you can better monitor your energy usage and bill.
How Does Your Home Compare to Others in the UK?
It doesn't follow that your household should use 3,731 kWh annually just because the average household in the UK does! Comparing your household to the average has its challenges because a small percentage of homes tend to use a disproportionately high quantity of electricity.
In light of this, it's wise to compare the energy consumption of your own home to a house of comparable size and design. The research shows that larger homes typically use more electricity, as you might anticipate.
The least amount of electricity is used by mid-terraces and flats, which each use about 2,800 kWh annually. End terraces consume a little bit more energy, followed by semi-detached homes, bungalows, and detached homes at 4,153kWh.
These numbers exclude heating. Of course, the numbers would be substantially greater if your home used electric heating. Knowing how you stack up won't actually help you use less electricity. We'll have to delve a little deeper into the statistics for that.

Ways to Cut Back on Energy Use
Even though there are numerous variables outside your control, there are a few certain techniques to cut your energy usage.
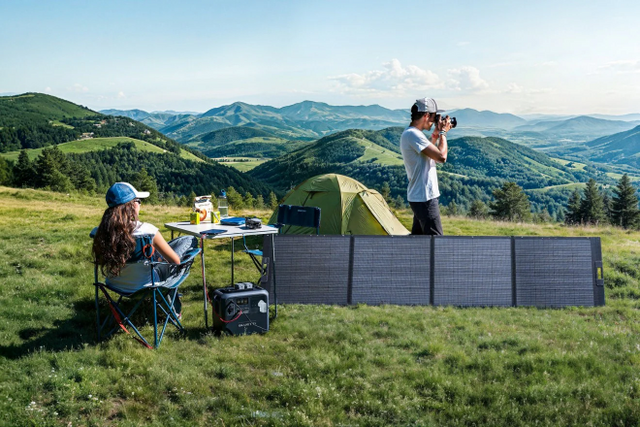
Solar Power Station
You can store electricity in an energy-storage system, often known as a power station, and utilise it later. You might be able to use the electricity your solar panels produce during the day by storing it for use at night.
The average electricity usage can be lowered impactfully if we used solar panels in our homes. However, the easiest way to start using solar energy is by installing a portable power station in your backyard. These are most commonly used when camping and living off the grid, but they can be used in any urban area as well, as a backup for your home, or for electricity savings. If you are confused about how to choose, this article maybe will give you an answer: 12 Best Solar Generators in the UK
Energy Saving Bulbs
To reduce their spending on electricity bills, a lot of consumers are switching to energy-efficient lighting. The majority of the electricity used by a typical incandescent bulb is typically converted into heat instead of light and therefore has a very short lifespan. Instead, you can choose CFL or LED bulbs, which each consume 75% and 80% less energy. These will cost you far less in the end because they last so much longer and save on your bills.
Switch off standby
By simply switching off your appliances' standby mode, you can save about £65 annually. Most electrical equipment can be turned off and used only when you actually need it. Items like a smart plug or a standby saver allow you to turn off all of your appliances' standby functions at the same time.
Use the Kitchen More Efficiently
A kettle is one of the most commonly used kitchen appliances in the UK. However, most of the time we fill the kettle with more water than we actually need, making it work longer and use more energy. By not overfilling the kettle, you can cut your annual electricity costs by £13.
Conclusion
Understand average electricity usage and the effects of your habits used to lower your bills. It is a more sustainable way of living if you understand how to save on electricity or start using power stations. In this time of energy uncertainty, it is an excellent strategy to have backup and not be constantly dependent on the electricity system in your hometown.
Shop products from this article
You May Also Like

Fridge Temperature Guide: What Temperature Should a Fridge Be?
Temperature management is crucial for the performance of the fridge. Find out at what temperature the fridge should be, the ideal range between 1-5°C, customised tips for winter, and the...

Winter Fuel Payment: Eligibility, Payment Dates, and Winter Energy Tips
Winter Fuel Payments are the best source for pension-age households to manage rapidly increasing winter energy costs. Explore more on the eligibility, payment dates, allowance amounts, and practical winter energy...

Sodium-Ion vs Lithium-Ion Battery: The Real Science behind Cold Weather Battery Drain
Why is sodium-ion battery often considered more reliable in winter? Do you know the real science behind it? In this guide, you will explore the comparison between lithium-ion and sodium-ion...